Radial Angiography (Wrist Angiography Method)
 20.09.2022
20.09.2022What is Angiography?
Angiography is the process of imaging the vessels feeding the heart, called coronary vessels. During the angiography procedure, while the patient is lying on his back, a special sheath is first infiltrated through the arteries in the groin or wrist, and then the catheter is advanced into the vein. When the catheter reaches the heart, a contrast agent is applied to show the inside of the vessel and imaging is performed under X-ray.
As a result of this procedure, called coronary angiography, the blockages in the vessels feeding the heart can be diagnosed definitively. In addition, angiography is a method used in the evaluation of valvular heart and aortic vascular diseases.
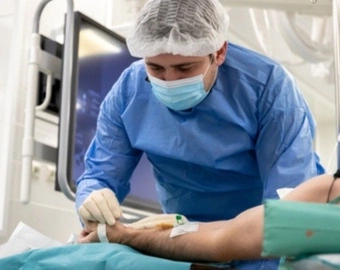
What is Wrist Angiography?
Wrist Angiography, also known as radial angiography, is the name given to coronary angiography performed through the radial artery through two arteries in the wrist. Wrist angiography was first used in 1989, and in 1996, it was accepted to be included in the coronary angiography methods for the first time. Wrist angiography is a procedure where the risks are not high. Today, it is preferred because it provides ease of application and is better for the patient’s comfort.
How is Wrist Angiography Performed?
During wrist angiography procedure, the subcutan is anesthetized using local anesthesia. A very small incision is made for the procedure, so there is no scar afterwards. During wrist angiography procedure, a catheter is inserted into the artery in the wrist and then this catheter is advanced to the heart vessel and the contrast agent is injected. During the procedure, X-rays are used to ensure the imaging of heart vessels on the screen.
After wrist angiography, the catheter is removed and the area where the catheter enters is closed with a bandage preventing the bleeding. The patient does not need to stay still, but it is still advisable to avoid activities that would put too much strain on the arm.
What are the Advantages of Wrist Angiography?
We can list the advantages of this procedure as follows:
- Patients can go to work or home 2-3 hours after the procedure.
- It is more comfortable for patients as there is no sandbag as in the groin.
- There is less chance of bleeding.
- Even if embolisation occurs in the wrist vein due to angiography, there will be no problem in the hand as the hand is fed through two vessels; however, if the inguinal vein is damaged, the leg may be at risk.
- It can be easily preferred in patients who are overweight in the abdomen and groin area or who have embolisation in the inguinal vessels.